Understanding Antioxidants: Boosting Health
Jul 17, 2025 / btwgardenmachine/
Antioxidants are a diverse group of compounds that play a crucial role in protecting our bodies from the damaging effects of free radicals. These molecules, produced through normal metabolic processes and environmental exposures, can wreak havoc on cells, contributing to aging and various diseases. Antioxidants act as a crucial defense mechanism, neutralizing free radicals and preventing them from causing oxidative stress.
Understanding the different types of antioxidants is key to appreciating their varied roles. From vitamins like vitamin C and E to minerals such as zinc and selenium, and even plant-based compounds like flavonoids and carotenoids, each plays a unique part in the body's intricate defense system. This wide range of antioxidants highlights the importance of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for optimal health benefits.
Sources of Antioxidants in Nature
Nature provides a wealth of antioxidant-rich foods. Berries, particularly blueberries and strawberries, are renowned for their high antioxidant content, offering a potent defense against cellular damage. Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale also contribute significantly to a healthy antioxidant intake.
Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, are another excellent source of antioxidants. These vegetables contain compounds that support detoxification processes and contribute to overall well-being. Incorporating these foods into your diet is a simple yet powerful strategy for boosting your body's antioxidant defenses.
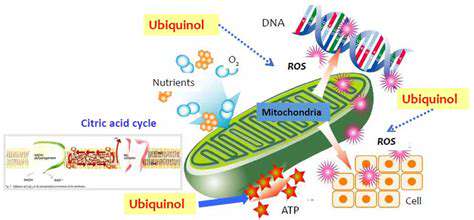
Antioxidant Roles in Cellular Health
Antioxidants work tirelessly within our cells to protect them from damage. They neutralize harmful free radicals, preventing them from attacking vital cellular components like DNA and proteins. This protective action helps maintain cellular integrity and function, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Maintaining healthy levels of antioxidants is crucial for preventing oxidative stress, a condition linked to aging and various diseases. This protection is especially valuable in combating chronic conditions and supporting the body's natural repair mechanisms. By supporting cellular health through antioxidants, you contribute to the body's ability to function optimally.
Antioxidant Benefits for Overall Health
The benefits of antioxidants extend beyond just cellular protection. They play a significant role in supporting immune function, reducing inflammation, and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and certain cancers. Studies have shown a correlation between higher antioxidant intake and a reduced risk of age-related decline.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While antioxidants are generally considered safe, excessive intake of certain supplements might not always be beneficial and in some cases, might even cause unwanted side effects. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before significantly increasing your intake of antioxidant supplements. Understanding the specific needs of your body is key to maximizing the benefits and minimizing any potential risks.
Furthermore, a balanced diet rich in whole foods is often the best way to obtain antioxidants naturally. Focusing on a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides a comprehensive array of nutrients, including antioxidants, and supports overall health in a more holistic way. Prioritizing natural sources over supplements is a prudent approach to ensuring optimal health benefits.
Observing your pet's physical cues is crucial in recognizing stress. Changes in posture, such as hunching, a tucked tail, or flattened ears, can indicate discomfort or anxiety. Notice if your pet exhibits excessive panting, tremors, or changes in their usual grooming habits. These physical manifestations often accompany underlying stress and can be subtle, requiring careful observation over time.
Beyond the Diet: Other Factors Affecting Antioxidant Levels
Lifestyle Choices and Antioxidant Intake
Dietary choices are crucial for antioxidant intake, but lifestyle factors play a significant role as well. Regular physical activity, for instance, can enhance the body's natural antioxidant defenses. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, can improve the efficiency of antioxidant enzymes and their ability to neutralize harmful free radicals produced during metabolic processes. This increased efficiency can lead to a more robust antioxidant system, which is beneficial for overall health and well-being.
Furthermore, adequate sleep is essential for optimal antioxidant function. When we sleep, our bodies repair and regenerate, including the maintenance and production of antioxidants. Chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt this process, potentially leading to lower antioxidant levels and increased susceptibility to oxidative stress. Prioritizing sufficient sleep, ideally 7-9 hours per night, is vital for maintaining healthy antioxidant levels and overall health.
Genetics and Antioxidant Capacity
Genetic predisposition can influence an individual's ability to produce and utilize antioxidants. Variations in genes involved in antioxidant enzyme production or the transport of antioxidants can affect the body's overall antioxidant capacity. While dietary and lifestyle choices are important, understanding these genetic factors can provide personalized insights into optimal antioxidant strategies.
Research in this area is ongoing, but it is becoming increasingly clear that genetic variations can significantly impact how the body processes and utilizes antioxidants. This knowledge is valuable for developing personalized recommendations for maximizing antioxidant intake and potentially mitigating the effects of genetic predispositions.
Stress Levels and Antioxidant Function
Chronic stress significantly impacts antioxidant levels. Stress hormones, like cortisol, can deplete the body's antioxidant reserves. Prolonged periods of stress can lead to increased oxidative stress, potentially damaging cells and contributing to various health issues. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help maintain healthy antioxidant levels.
Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress is crucial for maintaining optimal antioxidant function. Stress reduction strategies can help replenish antioxidant reserves and promote overall well-being.
Nutrient Interactions and Antioxidant Synergy
The effectiveness of antioxidants often depends on the presence of other nutrients. For instance, vitamin C enhances the absorption and utilization of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant. Consuming a balanced diet rich in various nutrients ensures that antioxidants work synergistically to protect the body from damage. This approach recognizes that individual antioxidants don't function in isolation but rather contribute to a comprehensive defense system.
Environmental Factors and Oxidative Stress
Environmental factors, such as exposure to pollution, air quality, and toxins, can increase oxidative stress in the body. These factors can lead to a higher production of free radicals, thereby requiring a greater antioxidant intake to counteract the damage. Living in areas with high air pollution, for example, may necessitate a greater focus on antioxidant-rich foods and practices.
Protecting oneself from environmental aggressors is crucial for maintaining healthy antioxidant levels. Making conscious choices about where one lives and works, as well as minimizing exposure to toxins, contributes to overall well-being. This includes not only dietary choices but also conscious choices about the environment one inhabits.
Supplementation Considerations
While a balanced diet is the cornerstone of antioxidant intake, supplementation may be considered in certain cases. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen. High doses of certain antioxidants can have adverse effects, and it's essential to ensure that the supplement is appropriate for individual needs and health conditions.
Supplements should be viewed as a potential adjunct, not a replacement, for a healthy lifestyle. They should be used in conjunction with a balanced diet and lifestyle choices to maximize the benefits of antioxidants and support overall health.